Discover everything you need to ace the chapter on India Size and Location with clear solutions, easy notes, and exam-ready summaries. This guide covers textbook answers, map skills, FAQs, and interactive quizzes, making it perfect for Class 9 students searching for quick revision, important questions, or complete study material on India’s geography and boundaries.
- EXERCISE: INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION Solved
- 1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
- 2. Answer the following questions briefly.
- 3. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
- 4. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
- MAP SKILLS
- PROJECT/ACTIVITY INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION
- FAQs about India Size and Location
- Mind map of the chapter for Quick Exam Revision
- Interactive Quiz on chapter 1 – India Size and Location
EXERCISE: INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION Solved
1. Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) The Tropic of Cancer does not pass through
(b) Odisha
(ii) The easternmost longitude of India is
(a) 97° 25′ E
(iii) Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, and Sikkim have common frontiers with
(c) Nepal
(iv) If you intend to visit Kavarati during your summer vacations, which one of the following Union Territories of India you will be going to
(b) Lakshadweep
(v) My friend hails from a country which does not share land boundary with India. Identify the country.
(b) Tajikistan
2. Answer the following questions briefly.
(i) Name the group of islands lying in the Arabian Sea.
Lakshadweep Islands
(ii) Name the countries which are larger than India.
Russia, Canada, USA, China, Brazil, Australia
(iii) Which island group of India lies to its south-east?
Andaman and Nicobar Islands
(iv) Which island countries are our southern neighbours?
Sri Lanka and Maldives
3. The sun rises two hours earlier in Arunachal Pradesh as compared to Gujarat in the west but the watches show the same time. How does this happen?
India has one standard time for the whole country. The time at 82°30′ E longitude is taken as Indian Standard Time. This is why, even though the sun rises earlier in the east, all watches in India show the same time.
4. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why?
India’s central position in the Indian Ocean helps it connect with countries of West Asia, Africa, and East Asia. It is important for trade, travel, and building strong relationships with other countries.
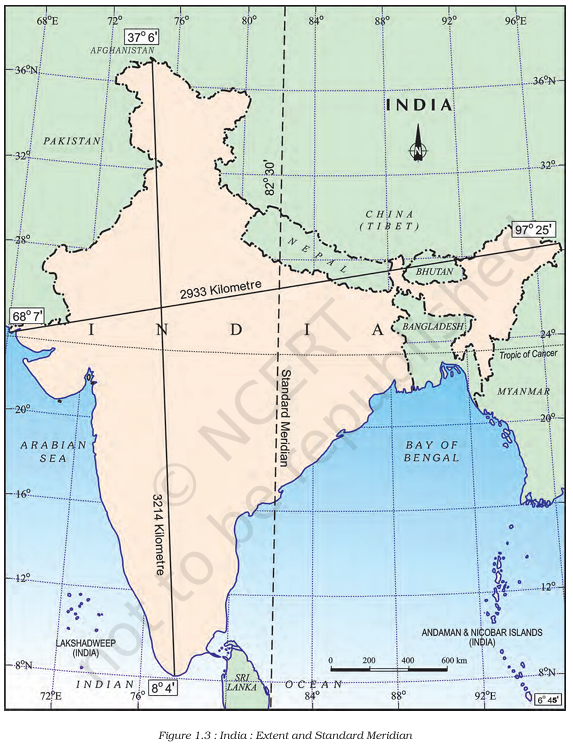
MAP SKILLS
(i) The island groups of India lying in the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal.
Lakshadweep (Arabian Sea)
Andaman and Nicobar Islands (Bay of Bengal)
(ii) The countries constituting Indian subcontinent.
India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives
(iii) The States through which the Tropic of Cancer passes.
Gujarat, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Tripura, Mizoram
(iv) The northernmost latitude in degrees.
37° 6′ N
(v) The southernmost latitude of the Indian mainland in degrees.
8° 4′ N
(vi) The eastern and the western-most longitude in degrees.
Easternmost: 97° 25′ E
Westernmost: 68° 7′ E
(vii) The place situated on the three seas.
Kanniyakumari
(viii) The strait separating Sri Lanka from India.
Palk Strait
(ix) The Union Territories of India.
Delhi, Chandigarh, Puducherry, Lakshadweep, Daman and Diu, Dadra and Nagar Haveli, Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Ladakh, Jammu and Kashmir
PROJECT/ACTIVITY INDIA SIZE AND LOCATION
(i) Find out the longitudinal and latitudinal extent of your state.
The answer will depend on which state is being asked. For example:
For Uttar Pradesh:
Latitude – between about 23°52’N and 30°28’N
Longitude – between about 77°3’E and 84°39’E
(ii) Collect information about the ‘Silk Route’. Also find out the new developments, which are improving communication routes in the regions of high altitude.
The Silk Route was an ancient trade route connecting India, China, and countries of Europe. It was famous for silk, spices, and other goods. Nowadays, new highways and tunnels are being built to improve communication and transport in hilly and high altitude areas, like the Atal Tunnel in Himachal Pradesh.
Here are 20 frequently asked questions and their answers about India, based on the provided information:
FAQs about India Size and Location
- What is India’s total land area?
India’s total land area is 3.28 million square kilometers. - How much of the world’s geographical area does India cover?
India covers about 2.4 per cent of the total geographical area of the world. - Which ocean is named after India?
The Indian Ocean is named after India. - What is the southernmost point of the Indian Union?
The southernmost point of the Indian Union is ‘Indira Point’. - Which parallel of latitude divides India into almost two equal parts?
The Tropic of Cancer (23°30’N) divides India into almost two equal parts. - Name the two island groups of India.
The two island groups of India are the Andaman and Nicobar islands and the Lakshadweep islands. - When did the Suez Canal open?
The Suez Canal opened in 1869. - What is the standard meridian of India?
The Standard Meridian of India is 82°30’E. - Name a country that shares a land border with India in the northwest.
Pakistan or Afghanistan shares a land border with India in the northwest. - What is the total length of India’s coastline?
The total length of India’s coastline, including islands, is 7,516.6 km. - How has India progressed in recent decades?
India has achieved great socio-economic progress in the last five decades. It has made remarkable advancements in farming, industry, technology, and overall economic growth. - How did ancient India connect with other parts of the world?
India had connections with the world for a long time, mostly through land routes. Mountain passes in the north allowed ancient travelers to exchange ideas and goods, while oceans limited interactions for a long time. - Why is India called the seventh largest country in the world?
India’s total land area is 3.28 million square kilometers, which is about 2.4 percent of the world’s total land area. This makes India the seventh largest country globally. - What are India’s neighbors across the sea?
India’s neighbors across the sea are Sri Lanka and Maldives. Sri Lanka is separated by a narrow channel called the Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar. Maldives Islands are located south of the Lakshadweep Islands. - How did the opening of the Suez Canal help India?
The opening of the Suez Canal in 1869 made travel between India and Europe much shorter. It reduced the distance by 7,000 km, making trade and contact easier. - Explain India’s strategic location in the Indian Ocean.
India has a very important central location between East and West Asia. It is like a finger extending into the Indian Ocean. The Deccan Peninsula sticks out into the ocean, allowing India to easily connect with West Asia, Africa, and Europe from its western coast. From its eastern coast, it can connect with Southeast and East Asia. India has the longest coastline on the Indian Ocean, which is why the ocean is named after it. - What ideas and goods did India share with the world in ancient times?
In ancient times, India shared many important ideas and goods with the world. Ideas from the Upanishads and the Ramayana, stories from Panchtantra, and the Indian numerals and the decimal system reached many other countries. India also sent out spices, muslin, and other goods to different parts of the world. - How do the various land boundaries and natural features define India’s geography?
India is a large country. It is bordered by young fold mountains in the northwest, north, and northeast. Towards the south, it narrows down and extends into the Indian Ocean. This ocean is then divided into two parts by India: the Arabian Sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. These natural features give India a unique geographical shape and position. - Describe the time difference across India and how it is managed.
There is a time difference of about two hours between Gujarat in the west and Arunachal Pradesh in the east. This is because of India’s wide east-west extent. To ensure everyone follows the same time, India uses a Standard Meridian. This is 82°30’E, which passes through Mirzapur in Uttar Pradesh. The time along this line is used as the standard time for the entire country. - What cultural influences has India received from other regions?
India, as an ancient civilization with long-standing connections, has also received cultural influences from other regions. For example, elements of Greek sculpture can be seen in India. Also, architectural styles like domes and minarets, which came from West Asia, are present in various parts of the country. This shows how India has absorbed ideas and styles from other cultures over time.
Mind map of the chapter for Quick Exam Revision

Interactive Quiz on chapter 1 – India Size and Location
Welcome to the Quiz!
Test your knowledge on India – Size and Location (Class 9) with 15 questions.
Each correct answer gets you 1 point.
The Geography Faculty at SolvedNotes is a team of subject matter experts dedicated to the CBSE Class 9 and 10 Geography curriculum. We specialize in decoding the NCERT textbooks ‘Contemporary India – I & II’, providing detailed insights into key topics like Physical Features of India, Climate, Drainage Systems, and Resources & Development. Our notes emphasize conceptual clarity on Agriculture, Manufacturing Industries, and Population dynamics. With a special focus on Map Work and data interpretation, we ensure students are fully prepared for both theory and map-based questions in their Board Exams.